| Acute Anterior Uveitis | |
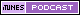
| Anterior uveitis is subdivided into iritis and iridocyclitis. In iritis the inflammation predominantly involves the iris and in iridocyclitis, the inflammation involves the iris and pars plica of the ciliary body equally. Acute uveitis has a sudden onset and persists for less than 6 weeks. Etiological factors include: trauma, infections with bacteria, fungi, virus protozoa, systemic collagen vascular diseases and unknown, idiopathic causes. The most frequent cause for acute anterior uveitis is idiopathic. The classical five symptoms of acute anterior uveitis are: pain, redness, watering, photophobia and blurring of vision. The typical findings include circumcorneal congestion, keratic precipitates, miosis, anterior chamber cells, flare, fibrin, hypopyon, posterior synechiae and anterior vitreous cells. This young male presented with acute anterior uveitis. All the investigations were normal. He was started on hourly topical steroids and cycloplegics. This photo was taken 5 days after his presentation. It shows marked circumcorneal congestion with contracting fibrin in the anterior chamber and a pupil in mid-mydriasis. | |
| Premsenthil, Mallika, M.D., Universiti Malaysia Sarawak¦2, Kuching, Malaysia | |
| H20.0 | |
| Iris and Ciliary Body -> Anterior Uveitis/Iridocyclitis -> Acute Anterior Uveitis/Iridocyclitis (see also Anterior Chamber) | |
| 7850 |
|
|||||||||||||||
Acute Anterior Uveitis-------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- -------------------------- |
|
||||||||||||||